Kidney Stones or Renal Calculi or Nephrolithiasis
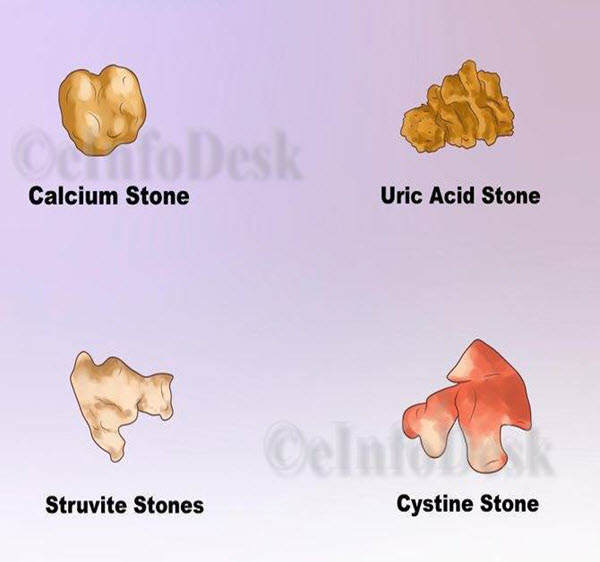
Depending on the material from which kidney stones are formed, they are classified into following types –
- Calcium: Calcium Stones are the most common type of Kidney Stones found everywhere. They are made up of Calcium Oxalate, Phosphate or Maleate. Calcium Oxalate stones are common among Calcium Stones. Vitamin C and Spinach contain oxalate. This stones most commonly occur in young men between ages of 20 and 30.
- Uric Acid: Uric Acid stones most commonly occur in Men than Women. These stones usually occurs in persons suffering from Gout or undergoing Chemotherapy.
- Struvite: Struvite Stones most commonly seen in Women with Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs). These Stones are quite large in size and can cause urinary obstruction.
- Cystine: Cystine Stones occurs in both men and women who have genetic disorder “Cystinuria”. But this Stones are very rare.
- Other Stones: Some Medications such as Triamterene and Acyclovir can also causes Kidney Stones.
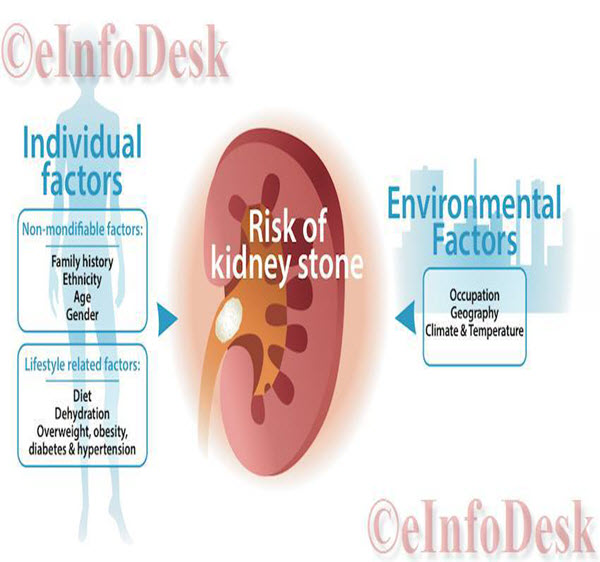
What Causes Kidney Stones: The risk factors for developing Kidney Stones are as follows
- Past History of Kidney Stones in Family Members – increases the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Less Water Consumption or Dehydration – leads to less water flow though kidneys which ultimately causes crystal deposition in kidneys.
- High Protein, Salt or Glucose Diet.
- Obesity.
- Gastric Bypass Surgery.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease – which increases Calcium Absorption.
- Other Medical Conditions like Hyperparathyroidism, which ultimately increases Calcium and Phosphorous Absorption.
- Renal Tubular Acidosis is also risk factor for Kidney Stones.
What Happens When Stones Formed in Kidneys: Kidney Stones usually causes radiating pain at the back particularly all over the position of kidneys. Kidney Stones never cause any symptom until they moves freely in kidneys and ureter. Symptoms of Kidney Stones include
- Severe pain in the side and back, below the ribs.
- Pain that spreads to the lower abdomen and groin.
- Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity.
- Pain on urination.
- Pink, red or brown urine.
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Persistent need to urinate.
- Urinating more often than usual.
- Fever and chills if an infection is present.
- Urinating small amounts of urine.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones: The Diagnosis of Kidney Stones Could be done from following Exams and Tests –
| Examinations | A Non-Contrast Spiral CT (Computerized Tomography) Scan | It is preferred method for kidney stones. It is special type of CT Scan which moves in Circle. |
| Ultrasound (U/S) Exam of Kidneys | It is also a preferred test as it exposes the patient to less radiation than the CT Scan. | |
| Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) | It is a X-ray test which shows pictures of Urinary Tract, including Kidney Stones. | |
| Retrograde Pyelogram | It is carried out if IVP and CT Scan doesn't provide a diagnosis. | |
| Abdominal X-Rays | It gives the picture of Kidneys, Bladder and the tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder (Ureters). | |
| Tests | Medical History | Physical Exam |
| Urine Collection, Urinalysis and Urine Cultures | To test the urine for presence of minerals and bacteria in exceeding quantities. To measure Volume, pH, Calcium Oxalate and Other Substances that have caused the stones to form. |
|
| Stone Analysis | Patient will be asked to collect stones by straining urine with fine-mesh gauze or strainer. | |
| Blood Chemistry Screen | To measure Kidney Function. To measure the levels of Calcium, Uric Acid, Phosphorous, Electrolytes and Other Substances that have caused the stones to form. |
Diet (DO & DON’T) followed in Kidney Stones:
Check out my next post, Top 10 Natural Remedies for Treatment and Prevention of Kidney Stones.